The Indispensables in Pianistic Success
The Indispensables in Pianistic Success? Are not the indispensables in all success very much the same? Nothing can take the place of real worth. This is especially true of America, in which country I have lived longer than in any other, and which, I am glad to call my home. Americans are probably the most traveled people of the world, and it is futile to offer them anything but the best. Some years ago a conductor brought to this country an orchestra of second-class character, with the idea that the people would accept it just because it bore the name of a famous European city which possessed one of the great orchestras of the world. It was a good orchestra, but there were better orchestras in American cities, and it took American audiences just two concerts to find this out, resulting in a disastrous failure, which the conductor was man enough to face and personally defray. The American people know the best, and will have nothing but the best. Therefore, if you would make a list of the indispensables of pianistic success in this country at this time you must put at the head of your list, REAL WORTH.
Musical Gifts
Naturally, one of the first indispensables would include what many term 'the musical gift' However, this is often greatly misunderstood. We are, happily, past the time when music was regarded as a special kind of divine dispensation, which, by its very possession, robbed the musician of any claim to possible excellence in other lines. In other words, music was so special a gift that it was even thought by some misguided people to isolate the musician from the world-to make him a thing apart and different from other men and women of high aspirations and attainments.
It is true that there have been famous prodigies in mathematics, and in games such as chess, who have given evidence of astonishing prowess in their chosen work, but who, at the same time, seem to have been lamentably under-developed in many other ways. This is not the case in music at this day at least, for, although a special love for music and a special quickness in mastering musical problems is indispensable, yet the musicians are usually men and women of broad cultural development if they desire it and are willing to work for it.
Nor can I concede that a very finely developed sense of hearing is in all cases essential. The possession of what is known as absolute pitch, which so many seem to think is a sure indication of musical genius, is often a nuisance. Schumann did not possess it, and (unless I am incorrectly informed) Wagner did not have absolute pitch. I have it, and can, I believe, distinguish differences of an eighth of a tone. I find it more disturbing than beneficial. My father had absolute pitch in remarkable fashion. He seemed to have extremely acute ears. Indeed, it was often impossible for him to identify a well-known composition if he heard it played in a different key-it sounded so different to him. Mozart had absolute pitch, but music, in his day, was far less complicated. We now live in an age of melodic and contrapuntal intricacy, and I do not believe that the so-called acute sense of hearing, or highly developed sense of absolute pitch has very much to do with one's real musical ability. The physical hearing is nothing; the spiritual hearing-if one may say so-is what really counts. If, in transposing, for instance, one has associated the contents of a piece so closely with its corresponding tonality that it is hard to play in any other tonality, this constitutes a difficulty-not an advantage.
Too much cannot be said about the advantage of an early drill. The impressions made during youth seem to be the most lasting. I am certain that the pieces that I learned before I was ten years of age remain more persistently in my memory than the compositions I studied after I was thirty. The child who is destined for a musical career should receive as much musical instruction in early life as is compatible with the child's health and receptivity. To postpone the work too long is just as dangerous to the child's career as it is dangerous to overload the pupil with more work than his mind and body can absorb. Children learn far more rapidly than adults-not merely because of the fact that the work becomes more and more complicated as the student advances, but also because the child mind is so vastly more receptive. The child's power of absorption in music study between the ages of eight and twelve is simply enormous; it is less between twelve and twenty; still less between twenty and thirty, and often lamentably small between thirty and forty. It might be represented by some such diagram as:
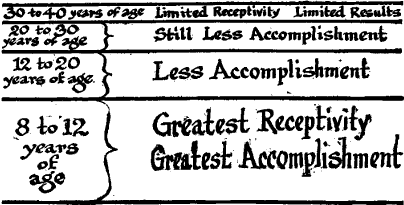
Of course, these lines are only comparative, and there are exceptional cases of astonishing development late in life, due to enormous ambition and industry. Yet the period, of highest achievement is usually early in life. This is especially true in the arts where digital skill is concerned.
Early Drill
All teachers are aware of the need for the best possible drill early in life. The idea one so often hears expressed in America: 'Since my daughter is only beginning her studies-any teacher will do,' has been the source of great laxity in American musical education. If the father who has such an idea would only transpose the same thought to the building of a house he would be surprised to find himself saying: 'Since I am only laying a foundation, any kind of trashy material will do. I will use inferior cement, plaster, stone, bricks, decayed wood and cheap hardware, and employ the cheapest labor I can procure. But when I get to the roof I shall engage the finest roofmakers in the world!'
The beginning is of such tremendous importance that only the best is good enough. By this I do not mean the most expensive teacher obtainable, but some one who is thorough, painstaking, conscientious, alert and experienced. The foundation is the part of the house in which the greatest strength and thoroughness is required. Everything must be solid, substantial, firm and secure, to stand the stress of use and the test of time. Of course, there is such a thing as employing a teacher with a big reputation and exceptional skill, who would make an excellent teacher for an advanced student, but who might be incapable of laying a good foundation for the beginner. One wants strength at the foundation-not gold ornaments and marble trimmings and beautiful decorations, fretwork, carving. Just as in great cities, one finds firms which make a specialty of laying foundations for immense buildings, so it is often wise to employ a teacher who specializes in instructing beginners. In European music schools this has almost always been the case. It is not virtuosity that is needed in the makeup, of the teacher of beginners, but rather sound musicianship, as well as the comprehension of the child psychology. Drill, drill, and more drill, is the secret of the early training of the mind and hand. This is indicated quite as much in games such as tennis, billiards and golf. Think of the remarkable records of some very young players in these games, and you will see what may be accomplished in the early years of the young player.
Meeting Obstacles and Complications
In all arts and sciences, as one advances, complications and obstacles seem to multiply in complexity until the point of mastery is reached; then the tendency seems to reverse itself, until a kind of circle carries one round again to the point of simplicity. I have often liked to picture this to myself in this way:

It is encouraging for the student to know that he must expect to be confronted with ever-increasing difficulties, until he reaches the point where all the intense and intricate problems seem to solve themselves, dissolving gradually into the light of a clear understanding day. This is to me a general principle underlying almost all lines of human achievement, and it appears to me that the student should learn its application, not only to his own but to other occupations and attainments. This universal line of life, starting with birth, mounting to its climax in middle life, and then passing on to greater and greater simplicity of means, until at death the circle is almost completed, is a kind of human program which all successful men would appear to follow. Perhaps we can make this clearer by studying the evolution of the steam engine.
The steam engine started with the most primitive kind of apparatus. At the very first it was of the turbine type. Hero of Alexander (Heron, in Greek) made the first steam engine, which was little more than a toy. According to some historians, Heron lived in the second century before Christ, and, according to others, his work was done in the latter half of the first century. He was an ingenious mathematician, who often startled the people of his times with his mechanical contrivances. It is difficult to show the principle of his engine in an exact drawing; but the following indicates in a crude way the application of steam force something after the manner in which Heron first applied it.
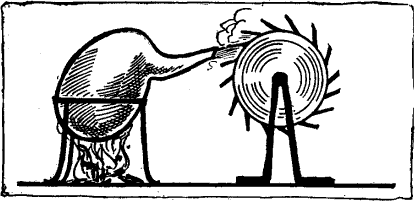
A is a retort containing water, which is heated to steam, which issues from the tube at B and is caught in the wheel in such a manner that the wheel revolves. The principle is simplicity itself; and the noteworthy fact is that-primitive as it is-it has the characteristic principle involved in the turbine engine of to-day. After Heron many others attempted to use controlled steam to produce force, until, in 1764, Jame Watt made discoveries which paved the way for the modern steam engine, constituting him virtually the inventor of the type. Thereafter, the machinery became more and more complicated and enormous in size. Double, triple and quadruple expansion types were introduced until, at the Centennial Exposition at Philadelphia, in 1876, a giant engine was exhibited by Corliss-a marvelous engine, with many elaborate details. Then, having reached the maximum curve of complexity, engine construction become more and more simple, and now we have turbine engines, such as the Parsons engines, which are ati far smaller and simpler than their grandfathers of the seventies, but at the same time vastly more powerful and efficient.
